
Analysis of application scenarios for skid-mounted equipment in the hydrogen energy chain, from production to refueling stations.
2025-12-22 11:59Analysis of application scenarios for skid-mounted equipment in the hydrogen energy chain, from production to refueling stations.
1. Production and Purification: Modular Solutions for Green and Blue Hydrogen
At the production stage, skid-mounted equipment offers unparalleled flexibility, which is critical for scaling both green and blue hydrogen projects. For green hydrogen production, modular electrolyzer skids are the cornerstone. These pre-assembled units integrate electrolysis stacks, power conversion systems, water purification units, and gas-liquid separators into a single, transportable package. This allows for the rapid deployment of multi-megawatt electrolysis capacity, significantly reducing on-site construction time and costs, especially in remote locations with abundant renewable energy. For blue hydrogen, which involves steam methane reforming coupled with carbon capture, the modular approach is equally vital. Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) skids can be seamlessly attached to the main hydrogen production unit to capture CO₂ emissions. Furthermore, regardless of the production method, hydrogen purification skids—utilizing Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) or membrane technologies—are essential for upgrading raw hydrogen to the high-purity levels (e.g., 99.97% for fuel cells) required for energy applications.
2. Storage, Transportation, and Conditioning: Ensuring Integrity and Delivery
Once produced, hydrogen poses unique challenges due to its low density and high permeability. Skid-mounted systems provide elegant solutions for conditioning and managing hydrogen at various logistical points. Compression skids are critical for boosting hydrogen pressure for pipeline transport or for high-pressure storage in tube trailers. These skids integrate multi-stage compressors with sophisticated cooling and sealing systems designed specifically for hydrogen service. For liquefaction plants, modular refrigeration and purification skids are used to cool hydrogen to extremely low temperatures (-253°C), a process that demands high efficiency and purity to prevent blockages. At the point of use, such as a refueling station, buffer storage skids and pre-cooling skids are essential. The pre-cooling units, for instance, chill the hydrogen to -40°C just before dispensing into a vehicle's tank, ensuring a fast, safe, and complete fill. The modular nature of these systems allows for scalable storage capacity and easy integration with different supply sources.
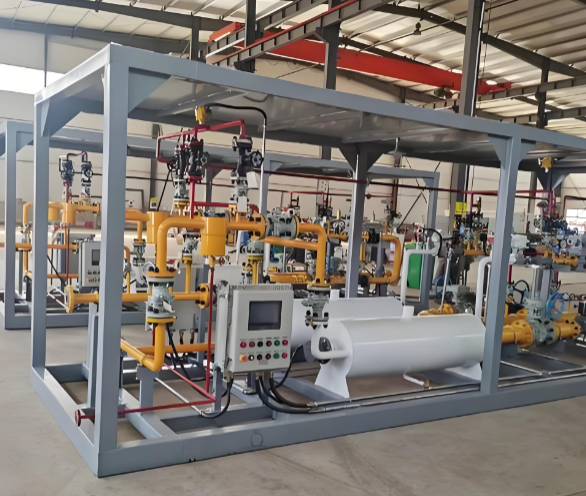

3. Dispensing and Refueling: The Modular Hydrogen Station
The refueling station is perhaps the most visible application of skid-mounted technology in the hydrogen chain, embodying the concept of a "gas station in a box." A complete hydrogen refueling station (HRS) skid integrates multiple functionalities into a compact footprint. This includes high-pressure storage vessels (often in a separate but connected module), a compressor skid, a pre-cooling skid, and the dispenser itself, all governed by a centralized safety and control system. The advantages are transformative. Stations can be pre-commissioned and tested at the factory, slashing on-site installation time from months to weeks. This modularity also allows for capacity to be easily scaled by adding more storage or compression skids as demand grows. Furthermore, it enables the deployment of stations in urban areas where space is limited, facilitating the adoption of fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs). For smaller-scale applications, such as back-to-base logistics fleets or industrial forklift charging, compact, all-in-one skid-mounted refuelers offer a cost-effective and rapidly deployable solution.
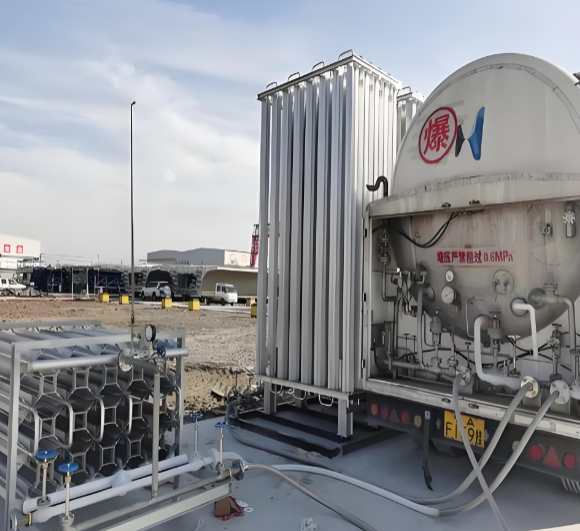

Summary
From production to purification, compression to dispensing, skid-mounted equipment is the indispensable building block of the emerging hydrogen infrastructure. Its core advantages—speed of deployment, scalability, standardized quality, and cost-effectiveness—directly address the key challenges of building a new energy network. By leveraging modular technology, the hydrogen industry can accelerate its growth, reduce capital risk, and create a flexible, adaptable ecosystem capable of evolving with technological advancements and market demands.
