
The Future of Natural Gas Infrastructure: How Skid-Mounted Systems are Revolutionizing Efficiency
2025-12-18 11:31The Future of Natural Gas Infrastructure: How Skid-Mounted Systems are Revolutionizing Efficiency
1. From Megaprojects to Modular Flexibility: Rethinking Infrastructure Delivery
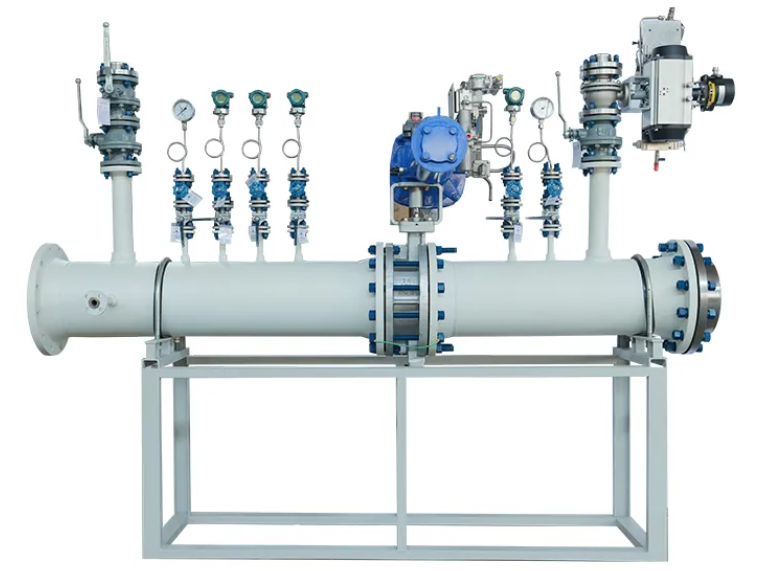
The traditional paradigm of natural gas infrastructure, characterized by vast, custom-built field installations, is being fundamentally reshaped. The shift is driven by the rise of skid-mounted, modular systems—pre-engineered, pre-tested functional units that deliver a plug-and-play alternative to stick-built construction. This modular approach is the cornerstone of efficiency. It transitions project execution from slow, sequential, and weather-dependent on-site assembly to a parallel process where skids are fabricated in controlled factory environments while site preparation occurs simultaneously. The result is a dramatic compression of the project timeline, often by 30-50%, and a significant reduction in capital cost uncertainty. This agility allows operators to respond swiftly to market opportunities, such as rapidly connecting new gas fields or deploying small-scale LNG facilities, with a scalable, repeatable, and lower-risk methodology. The era of the monolithic, decade-long megaproject is giving way to a more nimble, modular future.
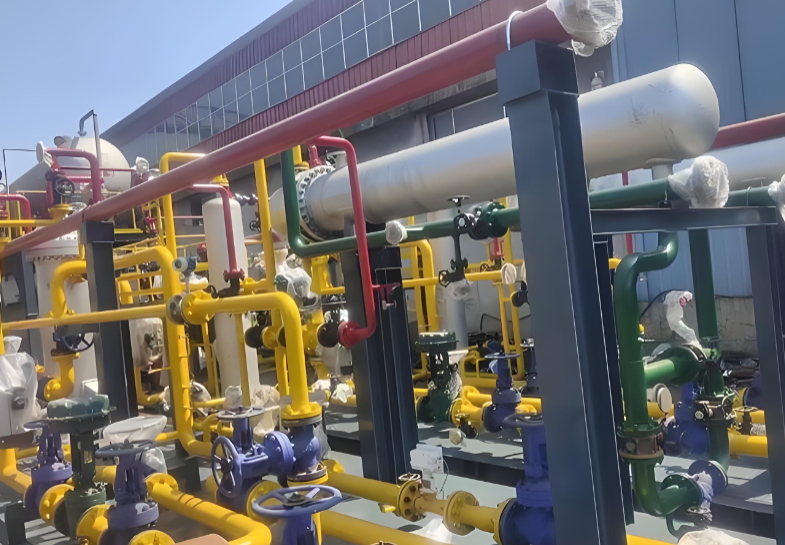

2. The Engine of Optimization: Standardization, Quality, and Smart Integration
Beyond speed, skid-mounted systems unlock a new tier of operational efficiency through standardization and enhanced quality. Factory fabrication ensures consistent, high-quality construction under strict protocols, with welds, instruments, and components assembled in optimal conditions, free from the variables of the field. This leads to superior system integrity, longer asset life, and reduced operational expenditures. Furthermore, modular design inherently promotes standardization. Repeating proven designs across projects creates economies of scale, simplifies spare parts inventory, and streamlines operator training. Crucially, the skid is the perfect vessel for digitalization. These pre-integrated modules are increasingly leaving the factory as "smart skids," embedded with sensors, control systems, and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) connectivity. This enables real-time performance monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote optimization, transforming a static piece of infrastructure into a dynamic, data-generating asset that maximizes throughput, safety, and uptime.
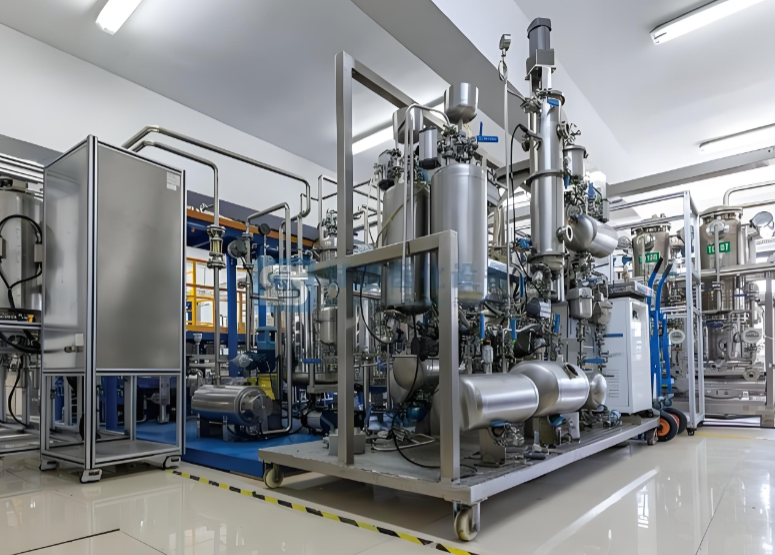

3. Enabling the Energy Transition: From Brownfield to Green Fuels
Skid-mounted modularity is proving to be a critical enabler for the evolving energy landscape. In traditional brownfield sites, these systems allow for efficient, low-disruption upgrades and capacity expansions without the need for prolonged shutdowns. More significantly, they are the platform of choice for emerging green fuel infrastructure. The production, conditioning, and distribution of hydrogen—whether blue, green, or in blends—heavily relies on skid-based solutions for rapid, cost-effective deployment. Similarly, modular carbon capture units, biogas upgrading systems, and small-scale gas-to-power plants are all leveraging this technology. Their scalability allows for pilot projects and incremental investment, reducing the financial and technical risk associated with transitioning to new energy systems. The inherent flexibility of skids means infrastructure can be adapted or relocated as supply and demand patterns change, protecting long-term investments in a dynamic market.
Summary
The future of natural gas infrastructure is not merely an evolution of scale, but a revolution in form and function. Skid-mounted modular systems are at the heart of this shift, delivering unmatched efficiency through accelerated deployment, guaranteed quality, and operational intelligence. By providing a scalable, standardized, and digitally native building block, they are not only optimizing traditional gas networks but also providing the essential agility needed to build the adaptable, integrated, and lower-carbon energy systems of tomorrow.
